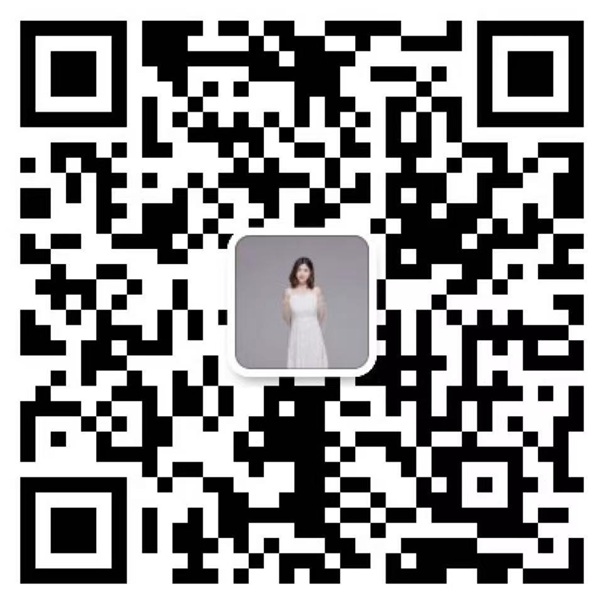
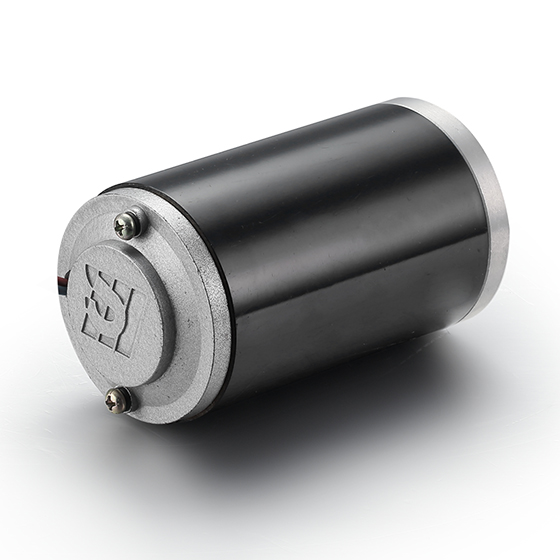
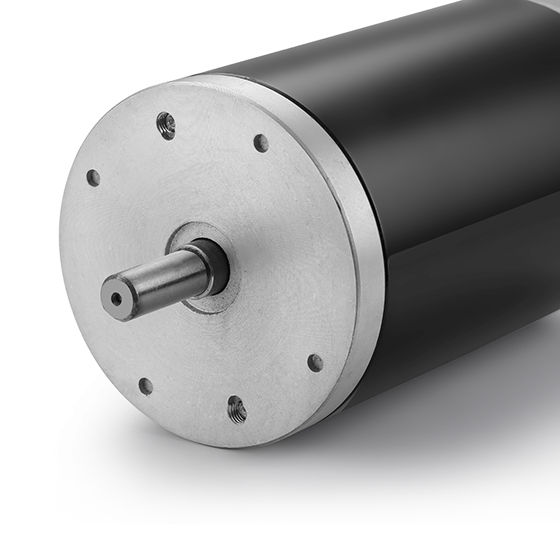
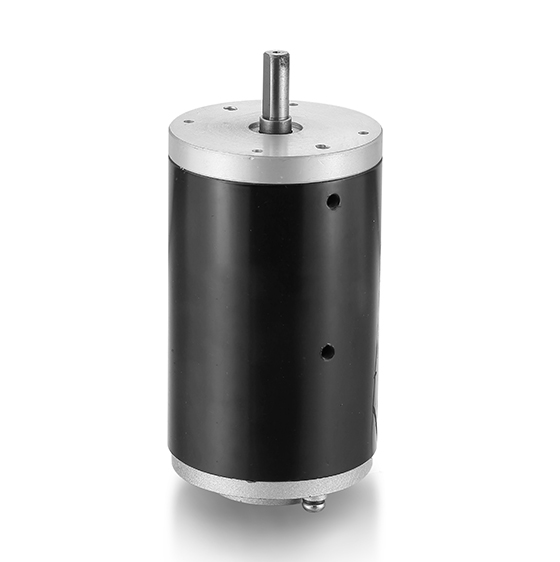
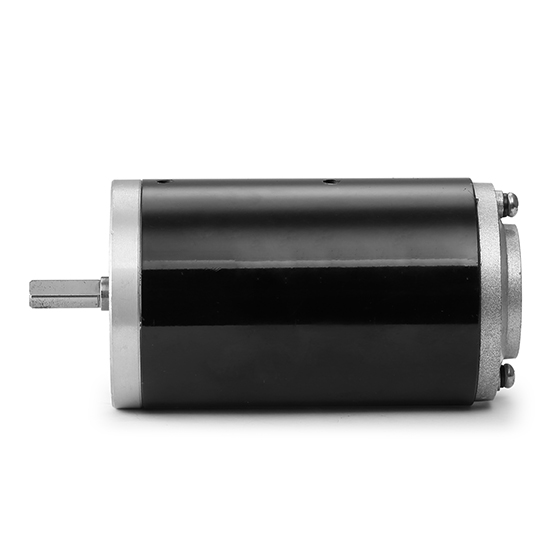
Description
| Environmental Conditons | —20℃~50℃ | Number of Phases | / |
| Rotation Direction | CW/CCW | Insulation Class | B-H |
| Noise | ≤65dB | Protection Class | IP40 |
| Work Condition | S1.S2.S3 |
Advantages
01Simple Structure:
The structure of DC brush motor is relatively simple, easy to manufacture and maintain. This makes it less costly, suitable for mass production and use.
02Easy Control:
The speed and torque of the DC brush motor can be easily controlled by adjusting the voltage and current. This makes it very popular in applications that require precise speed and position control.
03Large Starting Torque:
DC brush motor has high starting torque at low speed, which is suitable for applications that require high starting torque, such as electric vehicles, lifting equipment, etc
04Fast Response Speed:
Due to the small inertia of the motor, the DC brush motor has a very fast response speed and can quickly change the speed and direction.
05Wide Application:
Due to its simple structure, low cost and easy control, DC brush motors are widely used in various industrial and consumer electronic equipment, such as toys, power tools, small home appliances, etc.
06Easy Maintenance:
The maintenance and replacement parts (such as brushes) of DC brush motors are relatively simple, reducing downtime and repair costs.
Motor Technical Data
| Electrical Specifications | |||||||||
| Model | RATED LOAD | NO LOAD | STALL | ||||||
| Voltage | Power | Speed | Torque | Current | Speed | Current | Torque | Current | |
| V | W | rpm | N.m | A | rpm | A | N.m | A | |
| BG 63ZYT100 | 24 | 80 | 3000 | 0.25 | 4.76 | 4000 | 0.95 | 0.76 | 14.29 |
| We can also customize products according to customer requirements. | |||||||||
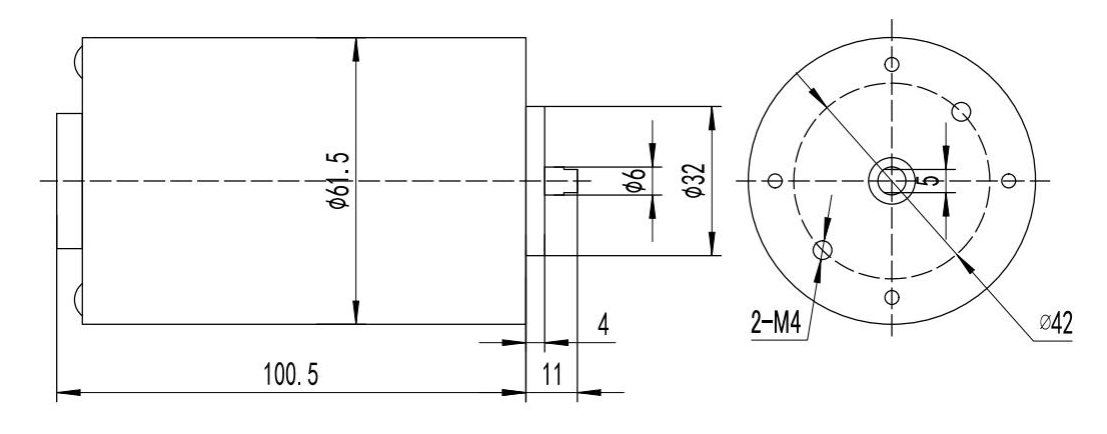
Mechanical Dimensions
Customizable solutions
Can provide custom voltage, electrical performance, circuit, etc.
And shaft, installation flange, lead wire, high-temperature class, drive, etc.
If you have any other needs, please contact our sales engineers.
Parts

Applications

Motor Selection Details
01Application scenarios:
Understand the specific application environment and use of motors, such as toys, power tools, home appliances, industrial equipment, etc.
02Voltage and current:
Determine the range of operating voltage and current required for the motor to ensure that the motor can operate normally under the customer's power system.
03Power and efficiency:
Determine the power and efficiency requirements of the motor according to the application requirements to ensure that the motor can meet the required working performance.
04Speed and torque:
Clarify the customer's speed and torque requirements for the motor, including the maximum speed, minimum speed, starting torque and working torque, etc.
05Size and installation:
Determine the overall size and installation method of the motor to ensure that the motor can adapt to the customer's equipment space and installation location.
06Life and reliability:
According to the customer's frequency of use and working environment, determine the life expectancy and reliability requirements of the motor, including the life of brushes and commutators.
07Environmental conditions:
Understand the working environmental conditions of the motor, such as temperature range, humidity, dust and water resistance level, etc., to select the appropriate motor type and protection level.
08Noise and vibration:
According to the customer's requirements for noise and vibration, choose a motor model with low noise and low vibration, especially in applications that require quiet operation.
09Control mode:
According to the customer's frequency of use and working environment, determine the life expectancy and reliability requirements of the motor, including the life of brushes and commutators
10Cost and budget:
Understand the customer's budget range to choose a cost-effective motor model to meet the customer's cost control requirements.
11Certifications and standards:
According to the application field and customer needs, determine whether the motor needs to comply with specific certifications and standards, such as CE, UL, RoHS, etc.
According to the customer's frequency of use and working environment, determine the life expectancy and reliability requirements of the motor, including the life of brushes and commutators













