Automation has revolutionized industries, bringing efficiency, consistency, and reduced labor costs. The growth of automation has driven an undeniable transformation across all sectors, providing immense competitive advantages.
Motors play a critical role in automation systems. Their performance and suitability directly impact the efficiency, reliability, and longevity of automated processes.
When selecting automation equipment and motors, manufacturers must carefully consider compatibility and performance. This article will explore the types of automation, the importance of motors, and key factors in selecting the right motor for your applications.
Automation can be categorized into six main types, each with its own structure, technology, advantages, and limitations. Understanding these will help manufacturers select the best automation system for their needs.

Fixed automation involves designing a system specifically for the production of a certain type of product. It uses dedicated equipment for repetitive tasks, offering high efficiency in mass production.
Advantages: Extremely efficient for large-volume production with minimal changeovers.
Disadvantages: Limited flexibility for product changes.
Application Example: Car manufacturing assembly lines.
Programmable automation allows flexibility in manufacturing by enabling the reprogramming of machines for different tasks or product types.
Advantages: Suitable for medium-volume production with moderate flexibility.
Disadvantages: More complex programming and setup.
Application Example: Electronic component manufacturing.
Flexible automation systems can be easily adapted to produce a variety of products. These systems can be reprogrammed or retooled for different production requirements.
Advantages: High flexibility, low downtime.
Disadvantages: Higher initial costs.
Application Example: Small-batch, custom production environments.
Collaborative robots (cobots) work alongside human operators, enhancing productivity while ensuring safety.
Advantages: Safety, flexibility, and ease of integration.
Disadvantages:Lower payload capacity than industrial robots.
Application Example: Picking and packing in warehouses.
Industrial automation uses control systems like computers and robots to handle processes in manufacturing plants. It increases the speed, precision, and efficiency of industrial operations.
Advantages: Consistent quality, higher production rates.
Disadvantages:High initial setup costs.
Application Example:Assembly lines in automotive or electronics industries.
Smart automation uses IoT (Internet of Things) technologies to collect data, enabling machines to adapt and optimize their operations autonomously.
Advantages: Real-time monitoring, predictive maintenance.
Disadvantages: High technology and integration costs.
Application Example: Automated warehouses with real-time data integration.

In automation, selecting the right motor is crucial for the efficiency and performance of the system. Motors commonly used in automation include:
DC Motors (Brushed and Brushless):Used for precise control of speed and torque.
Stepper Motors: Ideal for applications requiring precise position control.
Induction Motors: Commonly used in larger, high-power systems.
Servo Motors: Used for high-performance applications requiring precise positioning and speed control.
BLDC Motors (Brushless DC Motors):Preferred for high-efficiency, low-maintenance applications in robotics and automation systems.
Each motor type has distinct characteristics that make it suited for specific applications.
DC Motors:Provide good speed control and torque at low speeds, commonly used in applications like conveyors or robotics.
Stepper Motors: Offer precise control over position, making them ideal for 3D printers and CNC machines.
Induction Motors: Known for robustness and used in industrial automation where high torque and power are needed.
Servo Motors: Offer precise control over speed, position, and acceleration, making them perfect for robotic arms and CNC machines.
BLDC Motors: These motors are highly efficient, generate less heat, and have longer lifespans, making them ideal for automation systems that require high reliability with minimal maintenance.
Why BLDC motors are so popular in the field of automation?
Brushless DC motors (BLDC motors) are becoming more and more popular in the field of automation for the following reasons:
Brushless DC motors have higher efficiency than traditional brushed motors. This is because the brushless motor eliminates the friction between the brush and the commutator, reducing the waste of energy and allowing the motor to convert electrical energy more efficiently. For automation systems that require efficient energy utilization, BLDC motors are the ideal choice.
Since brushless DC motors do not have brushes, this means less friction and wear, which greatly increases the life of the motor. In automation applications, equipment often needs to operate for long periods of time, especially in a continuous working environment, so durability and maintenance become particularly important.
Since there are no brushes and commutators, the noise and vibration generated by BLDC motors during operation are much lower than those of brushed motors. This is especially important in some applications with high noise requirements (such as medical equipment, laboratory equipment, home appliances, etc.) to improve the comfort of the working environment of the equipment.
The brushless DC motor can be precisely controlled by an electronic controller to provide stable speed and position control. Precise control is a key requirement for automation systems, especially in applications that require high precision such as robotics, CNC machining, and 3D printing.
BLDC motors are typically designed to be smaller in size while being able to deliver greater power output, which makes them particularly valuable in space-constrained applications. For example, in AGVs (automated guided vehicles), robots, and other automated equipment, volume and weight control are very important factors.
Since there are no brushes, brushless motors require little maintenance. This is important for the operation of automated systems, especially in industrial environments where frequent maintenance or repairs are difficult, reducing downtime and maintenance costs.
The brushless DC motor can withstand higher temperatures and harsher working environments, and has good anti-interference ability. This makes them particularly suitable for use in industrial automation, especially in harsh environments such as chemical, mining or high humidity environments.
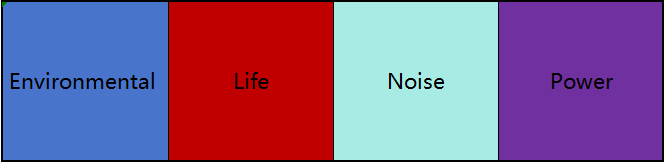
When selecting a motor for an automation system, consider the following factors:
Environmental Conditions: Humidity, dust, and pressure can affect motor performance. Ensure the motor is rated for the specific environment.
Motor Life: Look for motors with a long operational life and low maintenance requirements.
Noise and Vibration: Low noise and vibration are crucial for maintaining smooth operation in noise-sensitive environments.
Power Requirements: Ensure the motor provides the necessary torque and speed for the application.
Choosing the right motor for automation systems is a critical decision that impacts efficiency, performance, and maintenance. Understanding different types of motors and automation systems is key to selecting the best solution for your needs.
BG Motor has professional production experience and excellent quality service, in addition to the more common types of automated production motors in the market, we will also provide customized solutions according to the unique needs of customers, such as increasing the protective design of the protective case, increasing torque, minimizing noise, using green and pollution-free materials, and meeting the environmentally friendly standards.
In addition, we also have a huge material reserve, rich human resources, can achieve 20 days of delivery.
Therefore, if you have any needs, please contact us in time, we will be the most trusted motor supplier behind you.
 BACK
BACK
Electric Motors: The Backbone of Modern Machinery Electric motors power our wor…
Since its establishment in 1994, Bogong has been deeply involved in the …
Precision and power are essential in modern machinery. High torque motors fulfil…
Torque in a motor refers to the rotational force generated to perform work. It’s…
Thanksgiving in the United States is a major holiday, celebrated on the fourth T…
Alternating current (AC) powers nearly every modern device. However, many people…