Introduction: During the motor type test, there are many voltage points measured by the locked rotor test. When the motor is tested at the factory, a voltage point will be selected for measurement. Generally, the test is selected according to one-fourth to one-fifth of the rated voltage of the motor. Voltage, for example, when the rated voltage is 220V, 60V is uniformly selected as the test voltage, and when the rated voltage is 380V, 100V is selected as the test voltage.
The motor shaft is fixed and energized. The current at this time is the locked-rotor current. Common AC motors, including FM motors, are not allowed to stall. According to the external characteristic curve of the AC motor, when the AC motor is locked, a "subversion current" will be generated to burn the motor.
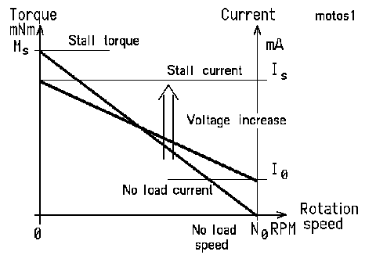
The value of stall current and starting current are equal, but the duration of motor starting current and stall current are different. The maximum starting current occurs within 0.025 after the motor is powered on and decays exponentially with time. , the decay speed is related to the time constant of the motor; while the locked-rotor current of the motor does not decay with time, but remains unchanged.
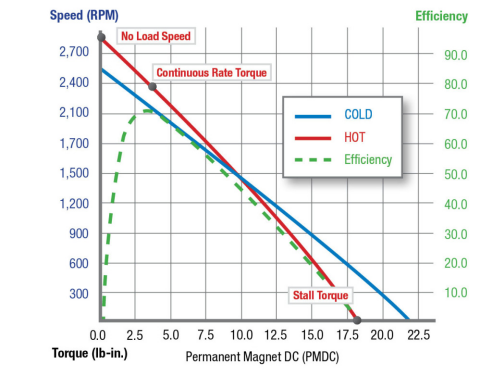
From the state analysis of the motor, we can divide it into three states: startup, rated operation and shutdown. The starting process refers to the process in which the rotor changes from a static state to a rated speed state when the motor is energized.
About motor starting current
The starting current is the current corresponding to the rotor changing from a static state to a running state at the moment when the motor is energized under the rated voltage condition. It is the process of changing the motion state of the motor rotor, that is, changing the inertia of the rotor, so the corresponding current will be relatively large. When starting directly, the starting current of the motor is generally 5 to 7 times the rated current. If the starting current of the motor is too large, it will have a great adverse effect on the motor body and the power grid. Therefore, for large and medium-sized motors, the starting current will be limited to about 2 times the rated current by means of soft start. The continuous improvement of the motor control system and various starting methods such as variable frequency start and step-down start have solved this problem well.
About motor stall current
Literally, the locked rotor current is the current measured when the rotor remains stationary, and the motor locked rotor is the situation where the motor still outputs torque when the speed is zero, which is generally mechanical or artificial.
When the motor is overloaded, the driven machinery fails, the bearing is damaged, and the motor has a sweeping fault, the motor may not be able to rotate. When the motor is locked, its power factor is extremely low, the locked rotor current is large, and the motor winding may be burned out for a long time. However, in order to test some performances of the motor, it is necessary to perform a stall test on the motor, which will be carried out in the type test and inspection test of the motor.
The stall test is mainly to measure the stall current, stall torque and stall loss under rated voltage. Through the analysis of the locked rotor current and three-phase balance, the stator and rotor windings of the motor, as well as the stator and rotor can be reflected. The rationality of the composition of the magnetic circuit and some quality problems.
If you are not clear about this, you can contact our professional sales staff, and BG motor sales staff will answer you in detail.
 BACK
BACK
In February 2025, BG Motor ushered in the traditional Lantern Festival celebrati…
The new year has begun, and BG Motor is officially back to work! After a refresh…
Dear Customers, Partners and Employees,On the occasion of the Spring Festival, B…
BG Motor, Ningbo, China, January 9, 2025 – As the festivities of Christmas and N…
At this juncture of saying goodbye to the old and welcoming the new, all BG Moto…
Originally commemorated the birth of Jesus, Christmas has become a powerful cult…