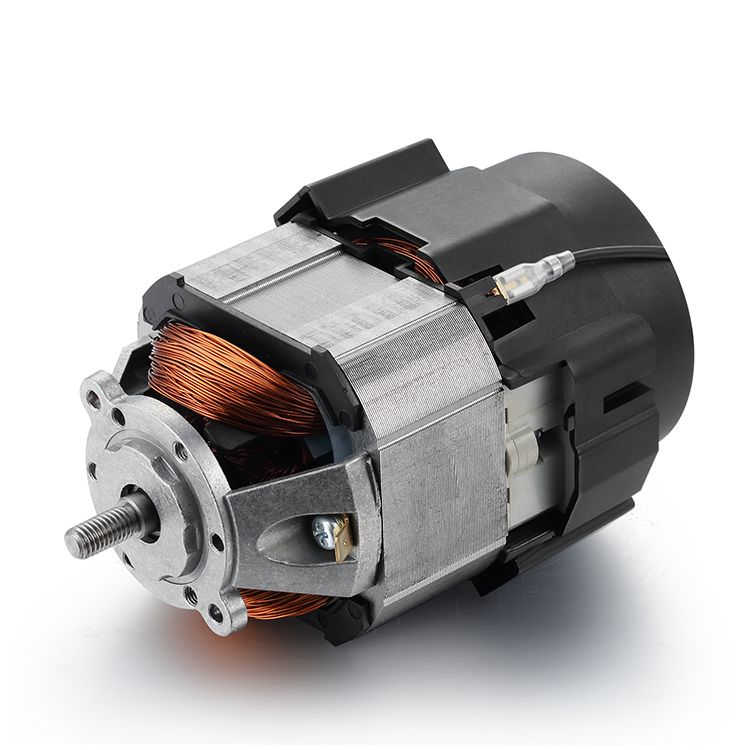
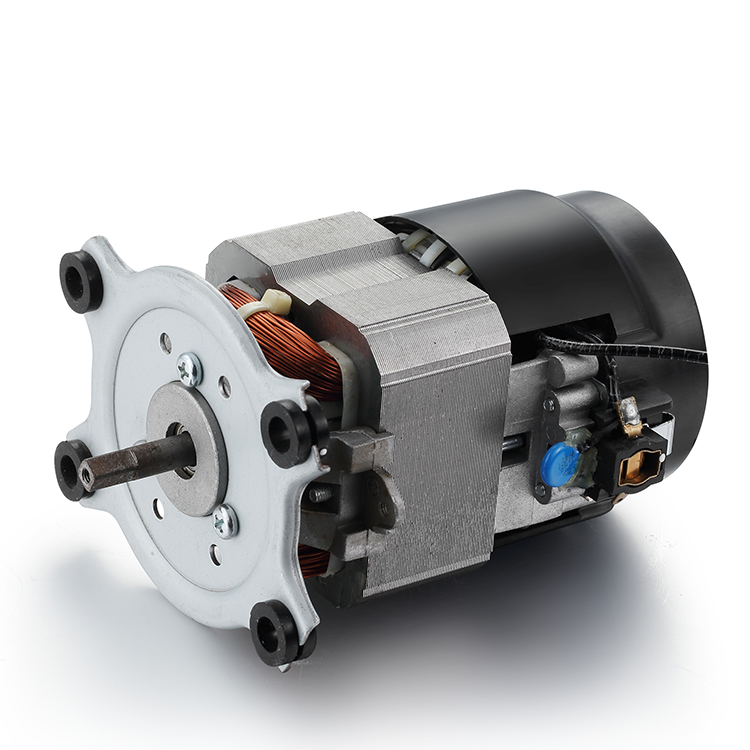
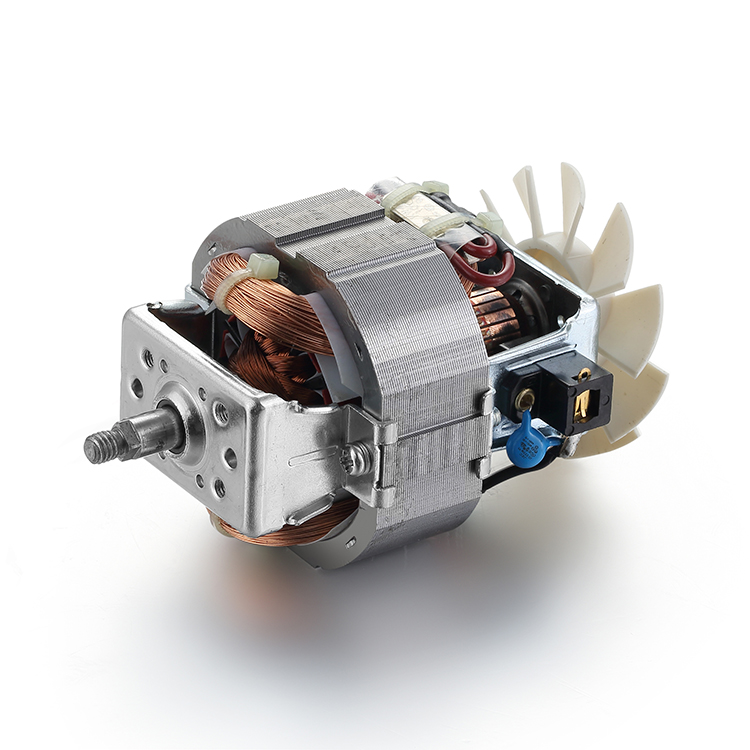
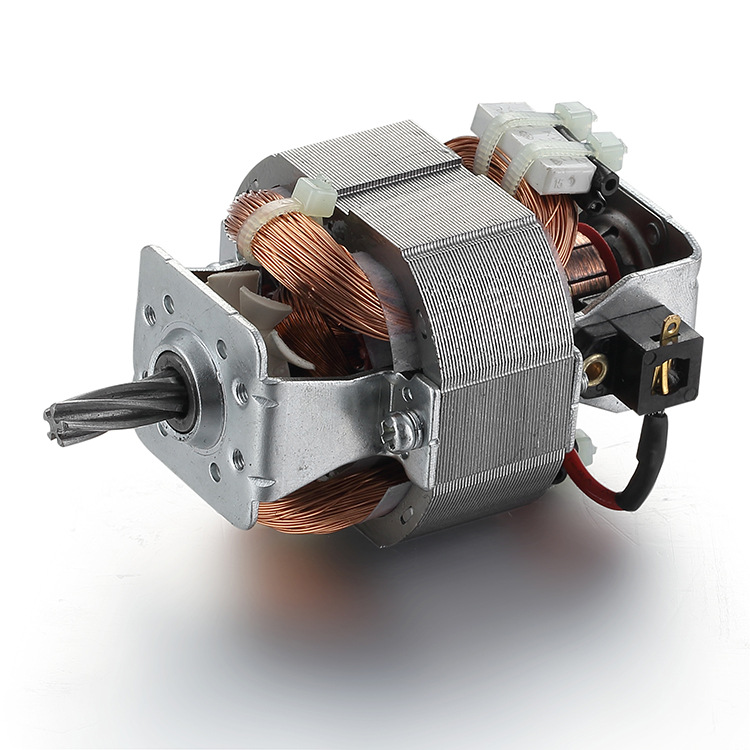
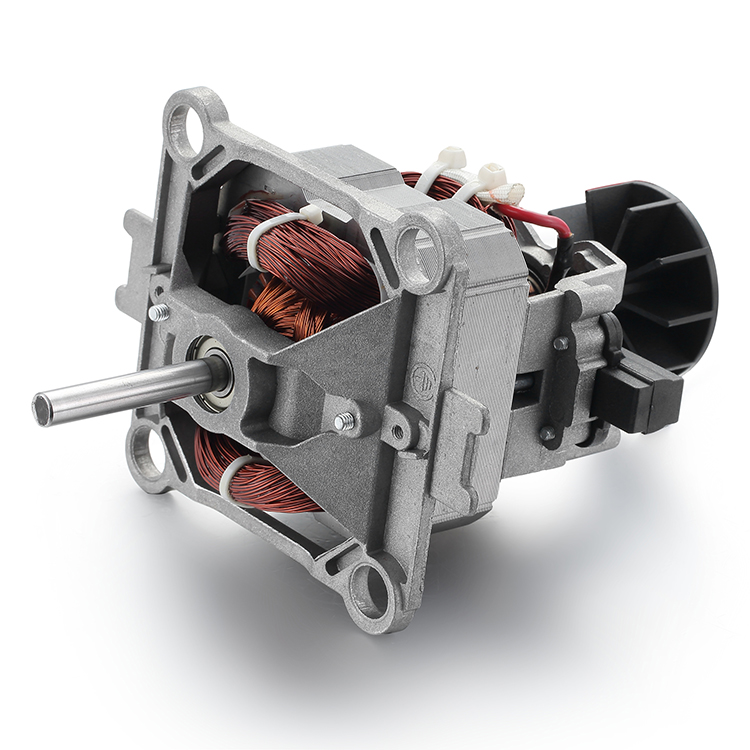
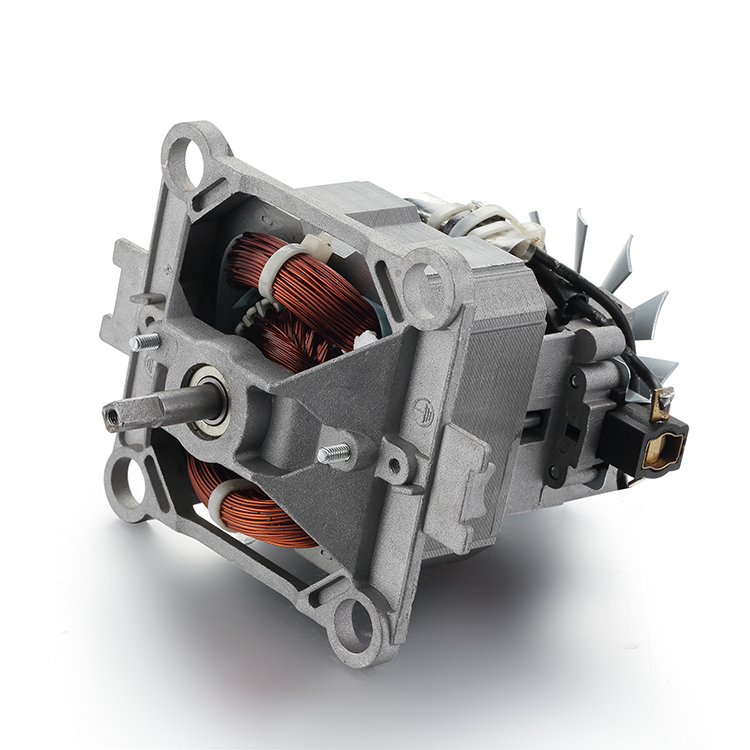
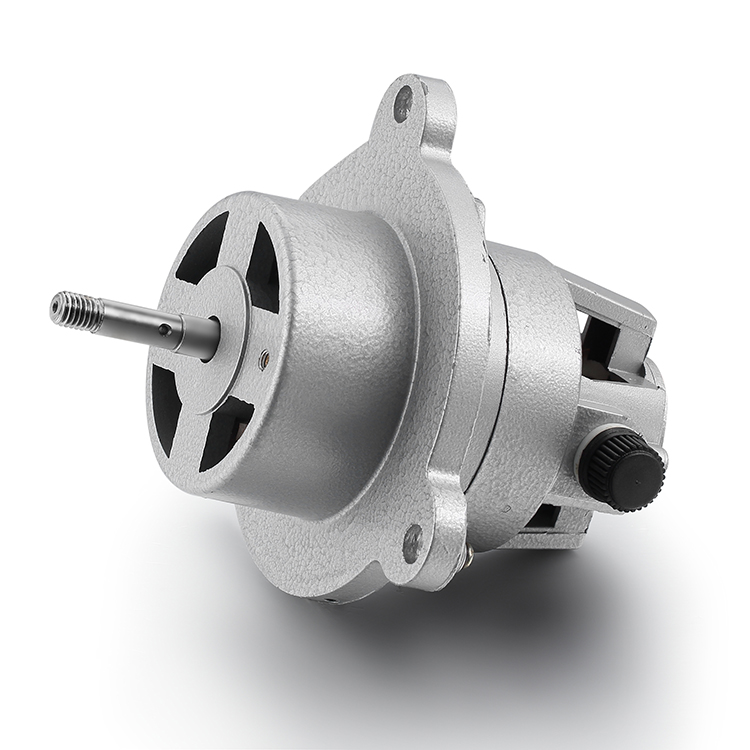
Description
| Environmental Conditons | —20℃~50℃ | Number of Phases | Single |
| Rotation Direction | CW/CCW | Insulation Class | B-H |
| Noise | ≤65dB | Protection Class | IP00 |
| Work Condition | S2.S3 |
Advantages
- 01High speeds:Single series motors are capable of reaching very high speeds, typically exceeding 20,000 RPM, making them particularly suitable for applications that require high-speed rotation, such as power tools and household appliances.
- 02High power density:Compared to other types of motors, single series motors can deliver higher power in a relatively small size, which makes them suitable for use in equipment that requires high power but where space is limited.
- 03Good starting performance: This motor has a high starting torque, so it is able to start quickly and reach working speed in a short time, which is important in some applications that require fast starting.
- 04Wide speed range: The speed of a single series motor can be flexibly controlled by adjusting the voltage or load, which makes it useful in applications that require a wide speed range.
05Simple construction and low cost:
Due to their relative simplicity of design and manufacture, single-item series motors typically have low production costs, which makes them attractive in many low-cost applications.
06Wide range of applications:
Due to their versatility and high performance, single series motors are widely used in a variety of household appliances such as vacuum cleaners, blenders, and hair dryers, as well as power tools such as drill bits and chainsaws.
07Overall:
Single-stage series motors are widely used in many applications that require high performance and flexibility due to their advantages such as high speed, high power density, good start-up performance, and cost-effectiveness.
Motor Technical Data
| Electrical Specifications | |||||||||
| Model | RATED LOAD | NO LOAD | STALL | ||||||
| Voltage | Power | Speed | Torque | Current | Speed | Current | Torque | Current | |
| V | W | rpm | N.m | A | rpm | A | N.m | A | |
| BGAC5421 | 110 | 150 | 12000 | 0.12 | 1.95 | 23000 | 0.39 | 0.36 | 5.84 |
| BGAC5425 | 220 | 200 | 12000 | 0.16 | 1.30 | 23000 | 0.26 | 0.48 | 3.90 |
| BGAC5430 | 220 | 250 | 12000 | 0.20 | 1.62 | 23000 | 0.32 | 0.48 | 4.87 |
| We can also customize products according to customer requirements | |||||||||
Mechanical Dimensions

Customizable solutions
Can provide custom voltage, electrical performance, circuit, etc.
And shaft, installation flange, lead wire, high-temperature class, drive, etc.
If you have any other needs, please contact our sales engineers.
Parts
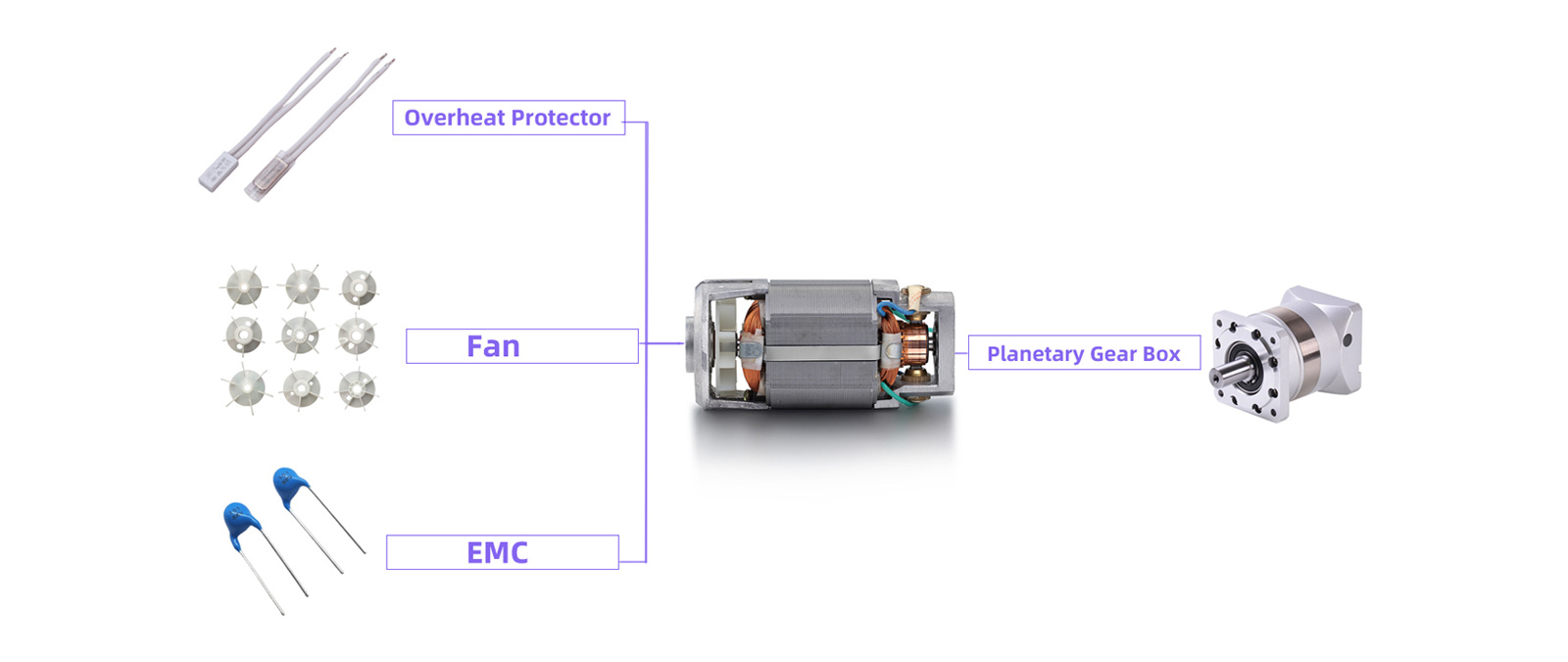
Applications

Motor Selection Details
01Application Scenarios:
Clarify what kind of equipment or application the motor will be used for (e.g., power tools, home appliances, etc.) in order to select the appropriate specifications and characteristics.
02Power Type and Voltage:
Determine the type of power (AC or DC) that the motor will be connected to and the operating voltage (e.g. 110V, 220V, etc.).
03Power requirements:
Understand the customer's power demand for the motor to choose the appropriate motor power level. The power required for the motor at maximum load needs to be determined.
04Speed:
Determine the speed range required for the application and ensure that the motor selected can meet these speed requirements.
05Starting Torque and Operating Torque:
Know the torque required by the motor when starting and running to ensure that the motor can provide enough force to start and run the load.
06Size & Installation Requirements:
Confirm the space constraints and installation requirements of the customer's equipment to select the appropriate motor size and installation method.
07Operating environment:
Understand the operating environment of the motor (such as temperature, humidity, dust, etc.) to select the type of motor and the level of protection suitable for the environment.
08Control mode:
Determine whether special control methods (such as speed adjustment, start control, etc.) are needed to select the appropriate control scheme.
09Life and reliability:
Understand the customer's requirements for motor life and reliability, so as to choose the appropriate motor brand and model.
10Cost And Budget:
Understand the customer's budget range to choose a cost-effective motor model to meet the customer's cost control requirements.
11Certifications And Standards:
According to the application field and customer needs, determine whether the motor needs to comply with specific certifications and standards, such as CE, UL, RoHS, etc.