Common faults of motors are divided into two categories: mechanical faults and electrical faults
Electrical faults include: short circuit, open circuit of the stator and rotor windings, and start-up equipment faults;
Mechanical failures include: excessive vibration, overheating of bearings, friction between stator and rotor, and abnormal noise.
Faults when the motor starts without load
1. Phenomenon: no sound and no rotation
①Check the voltage at the motor terminal with a multimeter. If there is no voltage or there is only one-phase voltage, it means that the power supply is not connected or the power supply is faulty;
②If the three-phase voltage at the motor terminal is basically balanced, it means that there is a problem with the motor stator winding connection. The most likely reason is that the neutral point is not connected or the lead wire is not connected.
2. Phenomenon: After the power is turned on, the motor only has a buzzing sound but does not rotate
The power must be disconnected immediately, and then carefully look for the cause
① For single-phase operation, first check the power supply to see if the power supply is one-phase disconnected, the fuse is one-phase blown, and the contactor is not in contact with one phase; then check the motor stator winding lead wire to see if one phase is not properly connected;
②Check if the machine part is jammed. When checking the motor before starting, it is easy to find that the power supply voltage is too low or the motor with the ▲-shaped connection method is connected in a Y shape and starts with a load. As long as the power supply voltage and motor wiring method are correct, it can be found.
3. Phenomenon: When the motor is started after power-on, the fuse will blow out quickly (or overcurrent protection action)
① Check that the rated current of the fuse does not match the capacity of the motor;
②Check whether the motor of the Y-connection method is mistakenly connected to the ▲ shape;
③The line between the motor power supply and the terminal has a phase-to-phase short circuit or a short circuit to the ground. Turn off the power switch, disassemble the motor terminal, and check with a megohmmeter to find out;
④ The motor stator winding or lead wire has a phase-to-phase short circuit or is grounded.
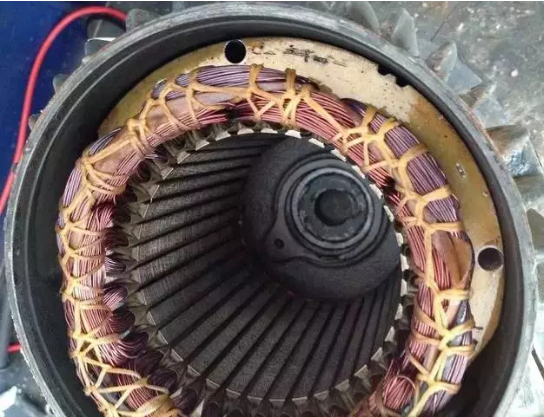

Abnormality in motor operation
During the operation of the motor, there will often be some abnormal operation phenomena, such as: motor vibration, motor overload, abnormal motor sound, temperature increase of bearing and wire circle, current increase and speed change, etc. These abnormalities will not cause the motor protection to operate. Tripping, but has affected the safe operation of the motor. Some important motors that run abnormally, if they are not handled in time, will not only cause the motor itself to malfunction, but also cause major accidents such as shutdown and shutdown of the furnace.
1. The motor runs without phase
Phenomenon: The ammeter indicates an increase or zero; the temperature of the motor body increases, and the vibration increases at the same time, and the sound is abnormal.
Treatment: The lack of phase operation of the motor is the operation mode of the three-phase motor when one phase of the circuit is disconnected due to some reason. First check whether the power supply lacks phase or the motor stator loop is faulty. One of the ways to prevent the motor from running under phase loss is to rely on the judgment of the attendant and deal with it in time after discovery; the second is to install a phase loss protector in the motor circuit.
2. The motor body heats up
Phenomenon: The body temperature and temperature rise of the motor during operation are significantly higher than those during normal operation, and the current increases.
deal with:
①Check whether there is friction or jamming on the mechanical load;
②Check whether the mechanical load increases, if so, reduce the load until the temperature is stable;
③Check whether the motor ventilation system is faulty, and reduce the load at the same time;
④Check whether the current of each phase of the motor is balanced, and judge whether the stator winding is faulty or the phase is missing.
3. The motor vibrates
①The motor is inconsistent with the mechanical center it carries;
②The motor rotor is unbalanced;
③The motor bearing is damaged;
④The motor foundation strength is not enough or the anchor screws are loose;
⑤ The motor runs without phase. If the motor vibration exceeds the allowable value range, the motor should be stopped immediately.
4. The motor sound is abnormal
① The mechanical reason of the motor: the sound of the bearing is abnormal. If it is caused by lack of oil, it should be refueled immediately; if the bearing is damaged, it should be stopped immediately;
②Electrical reasons: check whether the voltage and frequency are normal; check whether the three-phase stator current is balanced, and judge whether there is a wire break or an inter-turn short circuit inside the burning group...
 BACK
BACK
Electric Motors: The Backbone of Modern Machinery Electric motors power our wor…
Since its establishment in 1994, Bogong has been deeply involved in the …
Precision and power are essential in modern machinery. High torque motors fulfil…
Torque in a motor refers to the rotational force generated to perform work. It’s…
Thanksgiving in the United States is a major holiday, celebrated on the fourth T…
Alternating current (AC) powers nearly every modern device. However, many people…