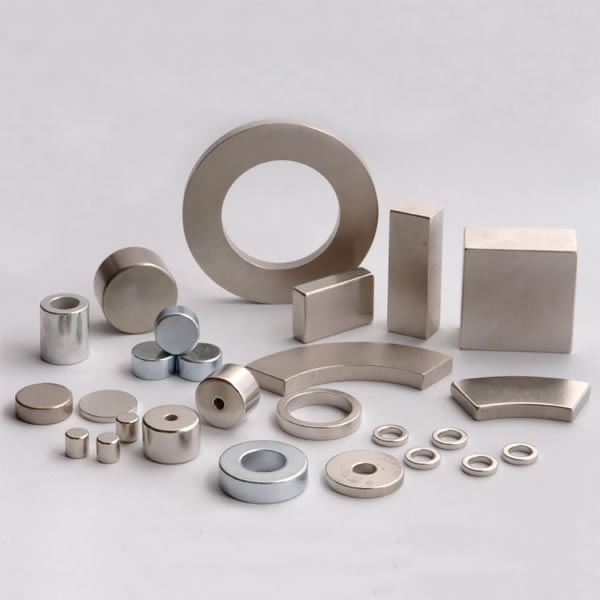
NdFeB, in simple terms, is a kind of magnet. The difference from the magnets we usually see is that it is called the "magnet king" because of its excellent magnetic properties. NdFeB contains a large amount of rare earth element neodymium, as well as iron and boron, and its characteristics are hard and brittle.
Since the surface is easily oxidized and corroded, NdFeB must be treated with surface coating. Surface chemical passivation is one of the good solutions.
As a kind of rare earth permanent magnet material, NdFeB has extremely high magnetic energy product and coercivity. At the same time, the advantages of high energy density make NdFeB permanent magnet materials widely used in modern industry and electronic technology, thus making instruments The miniaturization, weight reduction, and thinning of instruments, electro-acoustic motors, and magnetic separation and magnetization are possible.
The advantages of neodymium iron boron are high cost performance and good mechanical properties; the disadvantage is that the working temperature is low, the temperature characteristic is poor, and it is easy to pulverize and corrode. It must be improved by adjusting its chemical composition and adopting surface treatment methods. Meet the requirements of practical applications.
Neodymium iron boron magnetic material, as the latest result of the development of rare earth permanent magnetic materials, is called "magnet king" due to its excellent magnetic properties. The neodymium iron boron magnetic material is an alloy of praseodymium neodymium metal, boron iron and the like. Also known as magnet.

Classification:
NdFeB is divided into two types: sintered NdFeB and bonded NdFeB. Bonded NdFeB has magnetism in all directions and is resistant to corrosion; while sintered NdFeB is easy to corrode, and the surface needs to be coated, generally galvanized, Nickel, environmentally friendly zinc, environmentally friendly nickel, nickel copper nickel, environmentally friendly nickel copper nickel, etc. Sintered NdFeB is generally divided into axial magnetization and radial magnetization, depending on the required working surface.
NdFeB surface treatment:
With the thawing of patented technologies of sintered NdFeB in Japan, Germany, and the European Union, and the concerted efforts of major sintering manufacturers in my country, the grade of sintered NdFeB products has been greatly improved. As a high-tech application field, its comprehensive performance has been continuously improved, The requirements for the surface treatment of its sintered NdFeB have also been greatly increased, and the traditional treatment methods have been unable to meet the requirements of the progress of the industrial chain. The University of Electronic Science and Technology of China, Sichuan University, Jiaotong University, Rui Shilaisi and other scientific research institutions start from the micro-molecular structure. Essentially perfecting the principle of surface treatment and the development of industrial application processes, after 4 years of hard work, breakthroughs in key technologies have been achieved. Nano (3010) chelating films are treated without coating. This technology is an original technical process, nano film layer The active groups contained have strong resistance to moisture, oxygen, chloride ions (Cl), carbon dioxide (co2), etc. Corrosion resistance and the adhesion performance of organic resins are greatly improved. Its excellent surface physical and chemical properties will produce applications in the field Tremendous influence.

In December 2013, the treatment process was tested by Sichuan University and the Chinese Academy of Sciences. Its corrosion resistance can meet the requirements of 20-30 years of use in marine climate conditions. It can be widely used in sea-based wind power generation. The surface adhesion force is more than 20Mpa and can be widely used in permanent Magnetic high-speed motors, special motors, electric vehicle motors, UHV, high-voltage DC power supply systems, fast charging systems, aerospace and military industries.
Common surface treatment methods:
1, Nano (Royce3010) chelating film without coating treatment; (3010 means that the film contains more than three active chelating groups, and the thickness of the film is 10 nanometers);
2. Phosphating;
3. Electroplating;
4. Electrophoresis;
5. Vacuum vapor deposition;
6. Electroless plating;
7. Organic spray;
Application:
Sintered NdFeB permanent magnet materials have excellent magnetic properties and are widely used in electronics, electrical machinery, medical equipment, toys, packaging, hardware machinery, aerospace and other fields. The more common ones are permanent magnet motors, speakers, magnetic separators, Computer disk drives, magnetic resonance imaging equipment meters, etc.
Nano (Royce3010) chelating film non-plating treatment can meet the use of 20-30 years in marine climate conditions, and can be widely used in sea-based wind power generation. The surface adhesion force is more than 20Mpa, and it can be widely used in permanent magnet high-speed motors, special motors, and electric car motors. , UHV, HV DC power supply system, fast charging system, aerospace, military and other fields
Chemical composition:
The neodymium iron boron permanent magnet material is a permanent magnet material based on the intermetallic compound Re2Fe14B. The main components are the rare earth elements neodymium (Nd), iron (Fe), and boron (B). Among them, the rare earth element is mainly neodymium (Nd). In order to obtain different properties, some other rare earth metals such as dysprosium (Dy) and praseodymium (Pr) can be substituted. Iron can also be partially replaced by other metals such as cobalt (Co) and aluminum (Al). The content of boron is small, but it plays an important role in the formation of tetragonal crystal structure intermetallic compounds, making the compounds have high saturation magnetization, high uniaxial anisotropy and high Curie temperature.
The third-generation rare earth permanent magnet NdFeB is the most powerful permanent magnet in contemporary magnets. Its main raw material is rare earth metal neodymium 29%-32.5%, metal element iron 63.95-68.65%, non-metal element boron 1.1-1.2% and dysprosium 0.6-8% niobium 0.3-0.5% aluminum 0.3-0.5% copper 0.05-0.15% and other elements.
Folding discrimination:
1. It is usually placed on a surface that can be adsorbed with a magnet of the same specification, such as: patch, blade, iron gate, etc., to distinguish the size of the magnetic force by hand
2. Use electronic scales: Magnets with weak magnetic force are generally related to their density. If the density is low, the magnetic force will be relatively small. If the weight is heavy, the magnetic force will be relatively large. On the contrary, if the weight is light, the magnetic force will be small. The test was done.
Overview:
Each type of product is divided into several grades according to the maximum magnetic energy product
The grades of NdFeB magnetic materials are: N35-N52, 35M-50M, 30H-48H, 30SH-45SH, 28UH-35UH, 28EH-35EH.
Grade example: 048021 means (BH)max is 366~398kj/m3, Hcj is 800KA/m sintered neodymium iron boron permanent magnet material.
The grade of sintered NdFeB permanent magnet material is composed of three parts: the main name and two kinds of magnetic properties. The first part is the main name, which is composed of the chemical symbol ND of neodymium element, the chemical symbol of iron element FE and the chemical symbol of boron element B. The second part is the number before the line, which is the nominal value of the material’s maximum magnetic energy product (BH) max (unit: kj/m3), and the third part is the number after the diagonal line, the coercive force value of the magnetic polarization (unit: One tenth of KA/m), the value is rounded up.
Brand example: NdFeb380/800 means (BH)max is 366~398kj/m3, Hcj is 800KA/MR sintered neodymium iron boron permanent magnet material.
NdFeB surface treatment:
1. Phosphating;
2. Inorganic salt passivation;
3. Electroplating;
4. Electrophoresis;
5. Vacuum deposition;
Folding application:
Sintered NdFeB permanent magnet materials have excellent magnetic properties and are widely used in electronics, electrical machinery, medical equipment, toys, packaging, hardware machinery, aerospace and other fields. The more common ones are permanent magnet motors, speakers, magnetic separators, Computer disk drives, magnetic resonance imaging equipment meters, etc.
Curie temperature:
The Curie temperature of ferrite is 465℃,
The Curie temperature of NdFeB is 320°C-460°C,
The Curie temperature of AlNiCo is 800℃,
The Curie temperature of samarium cobalt is 700-800℃
The Curie temperature of FeCrCo is 680℃
Process flow:
Process flow: ingredients → smelting ingot/spinning belt → powder making → pressing → sintering and tempering → magnetic inspection → grinding processing → pin cutting processing → electroplating → finished product. Among them, the ingredients are the basis, and the sintering and tempering is the key.
NdFeB magnet blank production tools and performance testing tools: smelting furnace, belt spinning furnace, jaw breaking machine, jet mill, compression molding machine, vacuum packaging machine, isostatic press, sintering furnace, heat treatment vacuum furnace, magnetic performance test Meter, Gauss meter.
NdFeB magnet machining tools: centerless grinding, spheronization machine, double-end grinding, flat grinding, slicer, double-sided grinding, wire cutting, bench drill, special-shaped grinding, etc.
 BACK
BACK
Electric Motors: The Backbone of Modern Machinery Electric motors power our wor…
Since its establishment in 1994, Bogong has been deeply involved in the …
Precision and power are essential in modern machinery. High torque motors fulfil…
Torque in a motor refers to the rotational force generated to perform work. It’s…
Thanksgiving in the United States is a major holiday, celebrated on the fourth T…
Alternating current (AC) powers nearly every modern device. However, many people…