Torque in a motor refers to the rotational force generated to perform work. It’s essential for the motor’s ability to move loads, and understanding how it’s calculated helps in selecting the right motor for your application.
As we dive deeper into the technical aspects of motor performance, understanding the nuances of torque will help you make informed decisions about the motor that best suits your application. Let’s explore this concept further.
Speed and torque are two fundamental parameters used to describe a motor’s performance, but they represent different concepts. Speed refers to how fast the motor’s shaft turns, typically measured in revolutions per minute (RPM). Torque, on the other hand, refers to the rotational force exerted by the motor’s shaft.
In simple terms, speed is the rate at which the motor rotates, while torque is the force that enables the motor to rotate a load. They are interrelated, but not interchangeable. High-speed motors often produce lower torque, while motors designed for high torque might have lower speeds. This distinction is critical when choosing the right motor for specific tasks, such as lifting heavy objects or achieving high-speed rotation.
The choice between torque and speed largely depends on the application. Neither is inherently "better"—it’s about what is needed for the task.
High Torque: If you need a motor for tasks like lifting, turning heavy machinery, or driving gear systems, torque is more critical. A high-torque motor generates the necessary force to move heavy loads, even at lower speeds.
High Speed: If the goal is to achieve rapid rotation, like in fans, drills, or motors for precision instruments, speed becomes more important. A motor that runs at higher speeds may not need to generate as much torque, but it needs to rotate quickly for the system to perform as required.
In some applications, you may need both torque and speed, and this balance is essential for selecting the right motor for the job. The right motor specification is determined by the specific needs of your equipment.
Understanding how to calculate torque and speed in electric motors is essential for selecting the right motor for your application.
Torque Calculation: Torque can be calculated from the motor’s power and rotational speed using the formula:
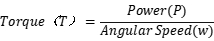
Where:
Power (P) is the motor’s output power (usually in watts).
Angular Speed (ω) is the speed at which the motor rotates, measured in radians per second.
If you know the motor's speed in RPM, you can calculate the angular speed in radians per second by converting it:
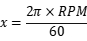
Speed Calculation: If you have the torque and power, you can find the motor’s speed using the rearranged formula:
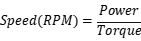
Using these formulas helps you understand the relationship between speed, torque, and power, giving you insights into how motor performance can be optimized for specific applications.
More torque does not necessarily mean more speed. While torque is the force required to rotate an object, speed is how fast that object rotates.
In many electric motors, increasing the torque may decrease the speed if the power supply remains constant. This is because the motor needs to exert more force, which can slow down the rotation. On the other hand, if you increase speed without adjusting torque, the motor might struggle to handle heavy loads.
For example, electric motors used in applications like power tools or electric vehicles require a balance between both torque and speed to ensure the system runs smoothly and efficiently.
Torque is related to both speed and power but is neither purely speed nor purely power. Torque is essentially a function of power and speed, with the equation connecting all three as follows:
P=T×w
Where:
· P is the power (in watts),
· T is the torque (in newton-meters),
· ω is the angular speed (in radians per second).
In this equation, torque plays a role in both power and speed. Therefore, understanding how to balance torque, speed, and power is essential for optimizing motor performance for your specific application.
When it comes to selecting the right motor for your application, BG Motor is a trusted name in the industry. Specializing in high-performance motors such as brushed DC motors, AC motors, and brushless DC motors, BG Motor provides customized solutions for a wide range of industries.
BG Motor offers a deep understanding of the relationship between speed, torque, and power, ensuring that each motor is tailored to meet the specific demands of your project. With expertise in motor design, manufacturing, and customization, BG Motor is dedicated to providing solutions that maximize efficiency and performance.
In conclusion, torque is a crucial aspect of motor performance, influencing both speed and power. Understanding how to balance these factors is essential when selecting the right motor for your needs. BG Motor provides expert solutions to ensure optimal motor performance.
If you have any needs, please contact us in time
 BACK
BACK
Electric Motors: The Backbone of Modern Machinery Electric motors power our wor…
Since its establishment in 1994, Bogong has been deeply involved in the …
Precision and power are essential in modern machinery. High torque motors fulfil…
Torque in a motor refers to the rotational force generated to perform work. It’s…
Thanksgiving in the United States is a major holiday, celebrated on the fourth T…
Alternating current (AC) powers nearly every modern device. However, many people…