Before introducing how to choose materials, let's first understand the composition of different materials.
1. Magnetic material: ferrite
Ferrite, also known as ferrite or magnetic porcelain, belongs to non-metallic magnetic materials. It is a composite oxide (or orthoferrite) of magnetic ferric oxide and one or more other metal oxides. Metal oxides with ferrimagnetism, the magnetic force is usually 800-1000 Gauss.
In terms of electrical properties, the resistivity of ferrite is much larger than that of single metal or alloy magnetic materials, and it also has higher dielectric properties. The magnetic properties of ferrite are also shown to have higher magnetic permeability at high frequencies. Therefore, ferrite has become a widely used non-metallic magnetic material in the field of high frequency and weak current. Due to the low magnetic energy stored in the unit volume of ferrite, the saturation magnetic induction (Bs) is also low (usually only 1/3 to 1/5 of pure iron), which limits its use at low frequencies that require higher magnetic energy density. It can be applied in the field of strong electricity and high power.
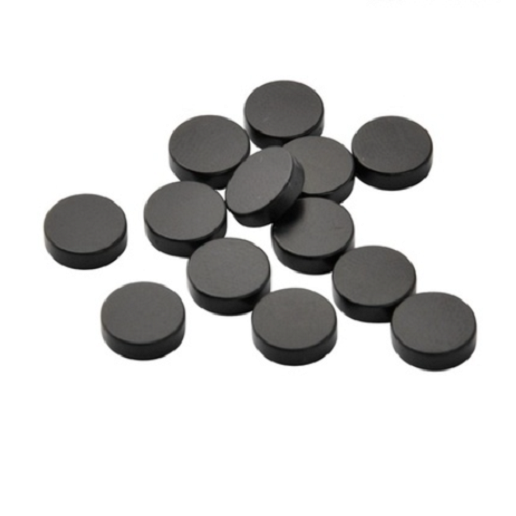

2. Magnetic material: NdFeB
NdFeB permanent magnet material is a permanent magnet material based on the intermetallic compound Nd2Fe14B. The main components are rare earth elements neodymium (Nd), iron (Fe), boron (B). Among them, the rare earth element is mainly neodymium (Nd). In order to obtain different properties, it can be partially replaced by other rare earth metals such as dysprosium (Dy) and praseodymium (Pr). Iron can also be partially replaced by other metals such as cobalt (Co) and aluminum (Al). The content of boron is small, but it plays an important role in the formation of tetragonal crystal structure intermetallic compounds, making the compounds have high saturation magnetization, high uniaxial anisotropy and high Curie temperature.
NdFeB is a high-performance rare earth material with high coercive force and high magnetic energy product, and the continuous improvement of this material in recent years has increased the use temperature and reduced the cost of the material. Applying NdFeB rare earth permanent magnet materials to the development of various motors can significantly reduce the quality of the motor, reduce the size of the motor, and obtain high-efficiency energy-saving effects and improve the performance of the motor.
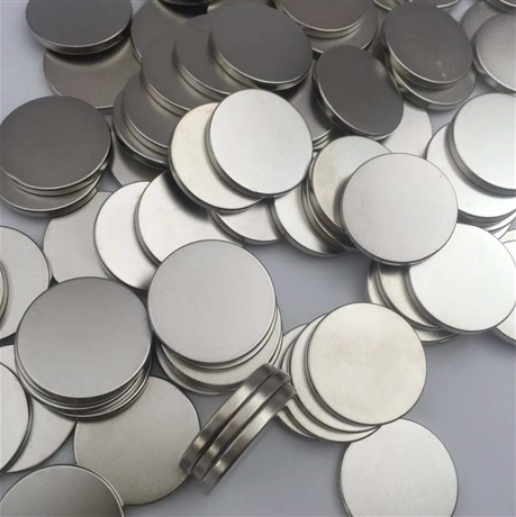

3. The difference between the two
The advantages of NdFeB are high cost performance and good mechanical properties; the disadvantages are that the Curie temperature is low, the temperature characteristics are poor, and it is easy to pulverize and corrode. It must be improved by adjusting its chemical composition and adopting surface treatment methods. , in order to meet the requirements of practical applications.
Ferrite is a metal oxide with ferromagnetic properties. In terms of electrical properties, the resistivity of ferrite is much larger than that of metal and alloy magnetic materials, and it also has higher dielectric properties. The magnetic properties of ferrite are also shown to have higher magnetic permeability at high frequencies. Therefore, ferrite has become a widely used non-metallic magnetic material in the field of high frequency and weak current.
NdFeB belongs to the third generation of rare earth permanent magnet materials. It has the characteristics of small size, light weight and strong magnetism. It is the magnet with the best performance and price ratio at present. The advantages of high energy density make NdFeB permanent magnet materials widely used in modern industry and electronic technology. In the state of bare magnets, the magnetic force can reach about 3500 Gauss.
Ferrite, also known as ferrite or magnetic porcelain, belongs to non-metallic magnetic materials, and is a composite oxide (or ferrite) of magnetic ferric oxide and one or more other metal oxides. The magnetic force is usually 800-1000 gauss, and it is often used in speakers, speakers and other equipment in addition to motors.
The general differences between NdFeB magnets and ferrite magnets are as follows:
( 1 ) The magnet performance of ferrite is poor, and the magnetic performance of neodymium iron shed is about 3 times that of ferrite.
( 2 ) In terms of price, the price of ferrite is much cheaper than that of NdFeB magnets.
( 3 ) NdFeB magnets have good temperature resistance, but demagnetization will occur if the working temperature exceeds a certain level. Therefore, it is recommended to choose a grade with a higher coercive force in a high-temperature working environment.
( 4 )The stability of ferrite is very good. It is an oxide itself, which is very stable. NdFeB is an alloy, and it is easy to oxidize, so it must be protected by coating.
Therefore, usually in the case of meeting the performance requirements of the motor, it is also necessary to consider better meeting the requirements of high cost performance. BG Motor's technical engineer team and business team will combine your requirements to customize and recommend suitable magnetic materials for you. Usually, brushless DC motors will choose high-performance NdFeB magnetic materials, and brushed DC motors will choose ferrite materials that are more economical; If some customers think that the control system of DC brushless motors is troublesome, we still The structure of the brushed DC motor can be customized, and the NdFeB magnetic material can be used, so that the torque of the motor can be larger, and it is easy to operate and use.
 BACK
BACK
In February 2025, BG Motor ushered in the traditional Lantern Festival celebrati…
The new year has begun, and BG Motor is officially back to work! After a refresh…
Dear Customers, Partners and Employees,On the occasion of the Spring Festival, B…
BG Motor, Ningbo, China, January 9, 2025 – As the festivities of Christmas and N…
At this juncture of saying goodbye to the old and welcoming the new, all BG Moto…
Originally commemorated the birth of Jesus, Christmas has become a powerful cult…