BG MOTOR
Model Number: BG 57BL01
Range of Power: .35-200W
Range of Voltage:12-310VDC
Range of Rated Speed: 12-750rpm
Range of Rated Torque: 0.4-17.8N.m
Lifespan: 5000-20000Hours
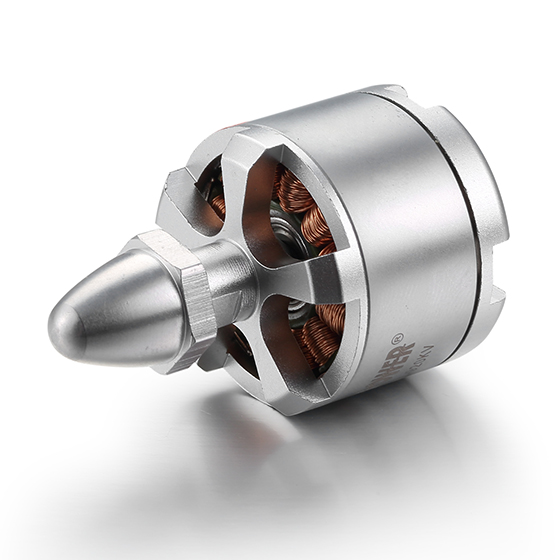

Model Number: BG 2212
Range of Power: 30-250W
Range of Voltage:6-24VDC
Range of Rated Speed: 3000-12000rpm
Range of Rated Torque: 0.04-0.3N.m
Lifespan: 5000-20000Hours
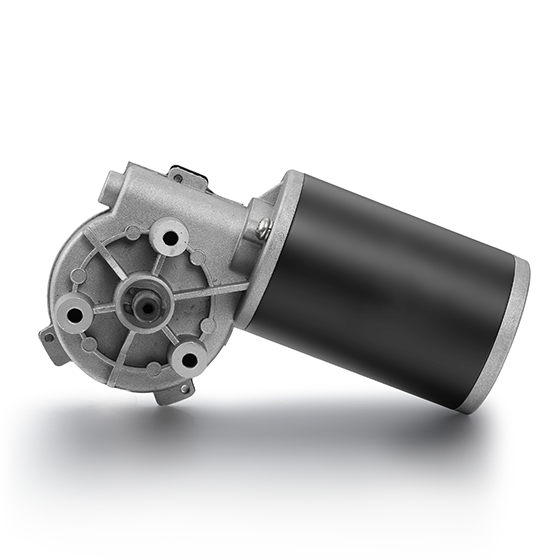

Model Number: BG 63ZYT125
Range of Power: 52-125W
Range of Voltage:12-110VDC
Range of Rated Speed: 50-100rpm
Range of Rated Torque: 4.65-9.3N.m
Lifespan: 1200Hours
Planetary Gear Motor
Model Number: BG 36BL95
Range of Power: 10-50W
Range of Voltage:12-4VDC
Range of Rated Speed: 22-750rpm
Range of Rated Torque: 0.4-5N.m
Lifespan: 3000Hours
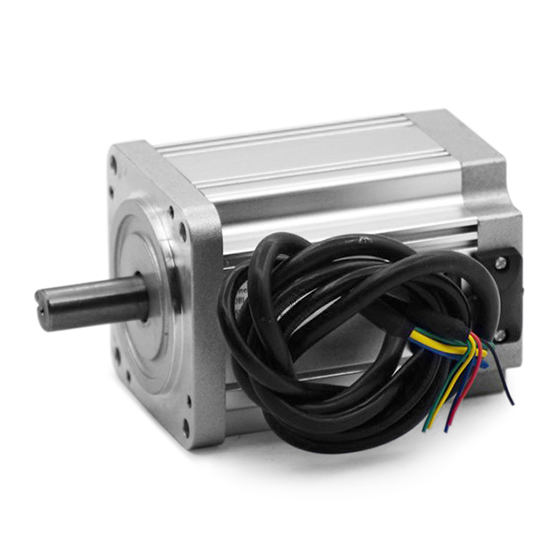

Model Number: BG 80BL110
Range of Power: 200-600W
Range of Voltage:12-310VDC
Range of Rated Speed: 1500-6000rpm
Range of Rated Torque: 0.64-1.7N.m
Lifespan: 5000-20000Hours
Model Number: BG 54ZYT82
Range of Power: 30-70W
Range of Voltage:12-48VDC
Range of Rated Speed: 2000-5000rpm
Range of Rated Torque: 0.19-0.45N.m
Lifespan: 1200Hours
Model Number: BG 58ZYT
Range of Power: 30-80W
Range of Voltage:12-48VDC
Range of Rated Speed: 3-750rpm
Range of Rated Torque: 0.49-12N.m
Lifespan: 1000Hours
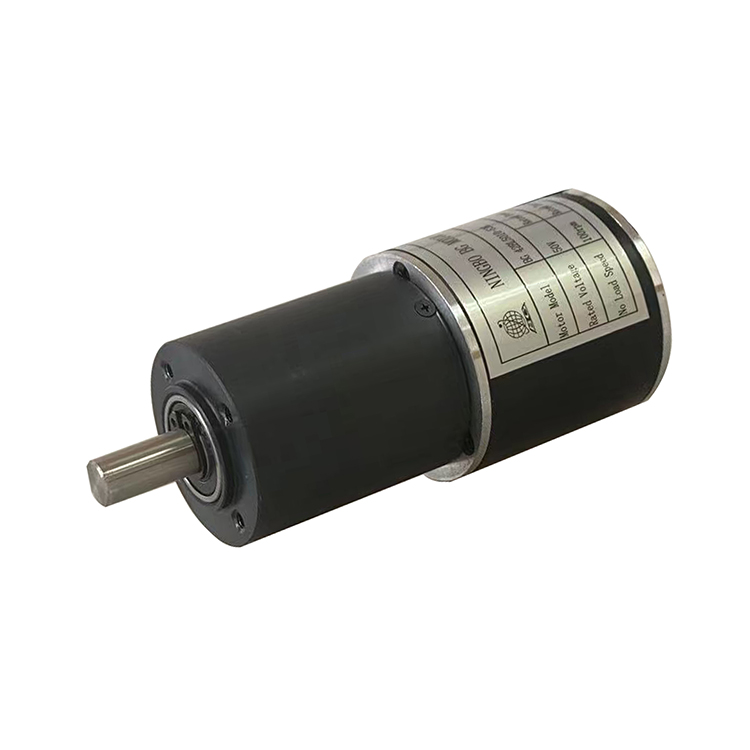

Model Number: BG 63ZYT125
Range of Power: 10-60W
Range of Voltage:12-48VDC
Range of Rated Speed: 1500-6000rpm
Range of Rated Torque: 0.03-0.2N.m
Lifespan: 5000Hours
Model Number: BG 90ZYT180
Range of Power: 100-300W
Range of Voltage:12-110VDC
Range of Rated Speed: 1500-4000rpm
Range of Rated Torque: 0.32-1.27N.m
Lifespan: 2000Hours
Model Number: BG 59ZYT96
Range of Power: 50-90W
Range of Voltage:12-48VDC
Range of Rated Speed: 1500-5000rpm
Range of Rated Torque: 0.32-0.57N.m
Lifespan: 1200Hours
Model Number: BG 28BL33
Range of Power: 5-30W
Range of Voltage:12-48VDC
Range of Rated Speed: 10-300rpm
Range of Rated Torque: 1-2N.m
Lifespan: 5000-20000Hours
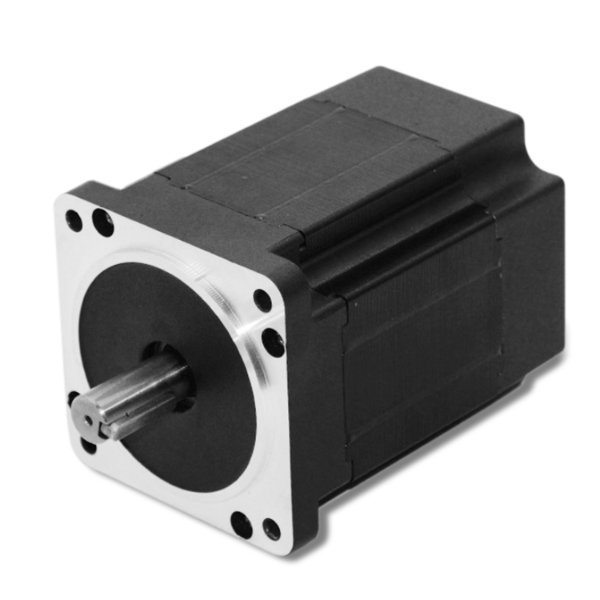

Model Number: BG 86BL105
Range of Power: 300-800W
Range of Voltage:12-310VDC
Range of Rated Speed: 1500-6000rpm
Range of Rated Torque: 0.65-2.5N.m
Lifespan: 5000-20000Hours
Model Number: BG 42BL80
Range of Power: 25-105W
Range of Voltage:12-48VDC
Range of Rated Speed: 1500-6000rpm
Range of Rated Torque: 0.06-0.33N.m
Lifespan: 5000-20000Hours
Model Number: 88-BG101
Range of Power: 150-350W
Range of Voltage:12-48VDC
Range of Rated Speed: 1500-4000rpm
Range of Rated Torque: 0.48-1.1N.m
Lifespan: 1000-1600Hours
Model Number: BG 555
Range of Power: 3-13.5W
Range of Voltage:12-24VDC
Range of Rated Speed: 3-330rpm
Range of Rated Torque: 0.4-5N.m
Lifespan: 1000Hours
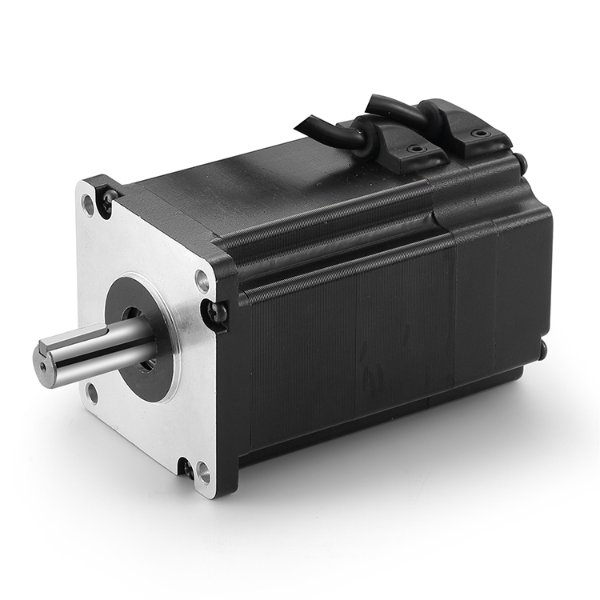

Model Number: BG 70BL01
Range of Power: 150-500W
Range of Voltage:12-310VDC
Range of Rated Speed: 1500-6000rpm
Range of Rated Torque: 0.48-1.59N.m
Lifespan: 5000Hours
What is a DC Motor?
A direct current motor is a type of electric motor that operates on direct current (DC). It converts electrical energy into mechanical energy through the interaction of magnetic fields. Here's a basic overview of how it works:
1. Basic components: DC motors typically consist of a rotor (or armature), stator, brushes, and commutator. The rotor is the rotating part of the motor, while the stator is the stationary part that generates the magnetic field. Brushes and commutators help to switch the direction of the current flowing through the rotor windings, which is essential for continuous rotation.
2.Operation: When a DC voltage is applied to the motor, the current flows through the rotor windings, generating an electromagnetic force. This force interacts with the magnetic field of the stator, causing the rotor to rotate. The commutator and brushes work together to ensure that the direction of the current in the rotor windings is constantly changing, thus maintaining continuous rotation.
3.Types of DC motors: There are many types of DC motors, including: DC brushed DC motors: use brushes and commutators to switch the direction of current. Brushless DC Motor (BLDC): Uses an electronic controller instead of brushes and commutators. With fewer friction parts, they tend to be more efficient and last longer. As well as the DC servo motor that adjusts the operating state of the motor in real time by the feedback system and the DC stepper motor that rotates the rotor step by step by sequentially excites the stator winding, so as to achieve accurate angle control.
4.Application: DC motors are widely used in various applications where speed control and smooth operation are important, such as electric vehicles, home appliances, robots and small machinery, different motors have different application places and best configurations, if needed, please contact our engineers for one-on-one communication.
5.Overall, DC motors are valued for their simplicity, ease of control, and ability to deliver a wide range of speeds and torques.
Types of DC Motors
There are several types of DC motors, each with unique advantages and applications:
It has a commutator and brushes that can switch the direction of current in the rotor windings, allowing continuous rotation. The electric energy of DC is through the brush and commutator into the armature winding, and the stator magnetic field interacts to produce torque, DC brush motor is simple and cost-effective, good control performance, smooth operation, high efficiency. However, due to the wear and tear of the brushes, it requires maintenance, and it is noisy and has a short life. It is mainly used in small electric equipment, remote control cars, electric drills, electric fans, etc.
Using an electronic controller instead of brushes and commutators, it is essentially an AC synchronous motor driven by an electronic drive with feedback control from position sensors. They offer high accuracy, high speed, high reliability, low noise, and require less maintenance, but they also increase technical complexity and manufacturing costs. It is suitable for electric vehicles, professional-grade drones, office automation equipment, medical instruments, high-speed centrifuges, and energy-saving household appliances for environmental protection purposes.
3. DC Servo Motor:
Similar to brushed or brushless motors, but equipped with a feedback system (such as an encoder) and a precision controller, it adjusts the operating status of the motor in real time through the feedback system to achieve high-precision control. It has the main advantages of high precision, high performance, and precise control of position, speed, and torque, but the system is complex and costly. It is widely used in automatic control systems, robots, aerospace.
4. DC Stepper Motor
The structure consists of multiple stator windings and segmented rotors (usually multipole). By sequentially exciteting the stator windings, the rotor rotates step by step to achieve precise angle control. Enables precise position control, good start and stop control. However, the speed range is limited, and vibration and noise may occur. It is widely used in printers, scanners, CNC machine tools, and CNC equipment.
5.Summary
-DC Brushed Motors: Ideal for cost-sensitive, easy-to-control applications.
-Brushless DC motor: suitable for high-efficiency, long-life, low-noise applications.
-DC Servo Motors: Ideal for applications that require high-precision and high-performance control.
-DC stepper motors: suitable for applications that require precise position control.
Brushed DC Motor is a traditional type of electric motor, and its main features include:
1.Structure and working principle
Stator: Usually composed of a permanent magnet or electromagnet that provides a fixed magnetic field.
Rotor: Contains brushes and commutator. The brushes are in contact with the commutator and are responsible for the commutation of the current.
Brushes and commutators: The brushes are in contact with the commutator and change the direction of the current to maintain the rotation of the rotor.
2. How it works
The electrical energy of direct current enters the armature windings through the brushes and steering gear, and interacts with the stator magnetic field to generate torque.
3. Pros & Cons
Advantages:
Simple structure: low design and manufacturing cost.
Simple control: no need for complex electronic control, easy to operate.
High starting torque: Able to provide high torque at start-up.
It is mainly manifested in wide control performance, wide speed regulation range, huge starting rotation, good vulgar performance, stable operation and high efficiency, and the application occasions are very wide from industrial to civil.
Disadvantages:
Wear and maintenance: Brushes and commutators are worn, frequent maintenance, and short life.
Low efficiency: Brush friction leads to energy loss and low operating efficiency.
Noise: Brush friction and electric sparks from the commutator can produce noise.
It is mainly manifested in high noise, short life, poor reliability, many faults, and frequent maintenance.
It is widely used in small electrical appliances, power tools, toys and other scenarios with low cost and maintenance requirements. Due to their simple design and low cost, DC brushed motors still have a place in many low-power and cost-sensitive applications.
Brushless DC motor (BLDC motor) is a new type of mechatronics motor that appears with the development of semiconductor electronic technology, which is the product of the combination of modern electronic technology (including power electronics and microelectronics technology), control theory and motor technology. It is widely used in applications that require high efficiency, long life, and low maintenance. In contrast to traditional Brushed DC motors, BLDC motors do not have brushes and commutators, which are common wear and tear parts in conventional motors.
The following is the basic concept of BLDC motors:
1.Structure and working principle
Stator: The stator of a BLDC motor is equipped with electromagnetic coils (multiphase windings) that generate a rotating magnetic field when the motor is running.
Rotor: The rotor of a BLDC motor is equipped with a permanent magnet that generates rotation through interaction with the magnetic field of the stator.
Sensors & Controllers: In order to accurately control the operation of the motor, BLDC motors are usually equipped with position sensors (e.g., Hall sensors) and electronic controllers (ECUs). The controller adjusts the current flow into the stator's coil based on the feedback from the sensor, thus controlling the speed and direction of the motor.
Therefore, a brushless DC motor is essentially an AC synchronous motor driven by an electronic inverter with feedback control from a position sensor.
2. Advantages;
High efficiency: The motor is more efficient due to less energy loss due to the absence of brushes and commutators.
Long life: Reduced wear parts, BLDC motors generally have a long service life.
Low maintenance: Brushless motors have less maintenance requirements and lower failure rates due to the absence of brushes.
High speed and high power density: Able to operate at higher speeds and provide high power output.
3. Application scenarios
Electric Vehicle: The wheels used to drive an electric vehicle.
Household appliances: such as vacuum cleaners, air conditioning fans, etc.
Drones: provide stable and efficient power.
Computer equipment: Drives for fans and other internal components.
4. Control mode:
Open-loop control: simple control method, no feedback information required. Typically used for low power and simple applications. Closed-loop control: Feedback sensors, such as Hall sensors, are used to adjust motor operating parameters in real time to ensure accurate control of speed and position.
5. Disadvantages:
Higher cost: The initial cost is usually high due to the need for electronic controllers and sensors.
Complexity: Complex control systems are required, making design and commissioning difficult.
-The rotor permanent magnet material limits the ambient temperature of the motor and is not suitable for high-temperature fields
BG Motor——Professional high quality DC motor manufacturer
Resolutely work together with customers to overcome various difficulties
Since its establishment in 1994, with more than 30 years of R&D experience, we continue to invest in R&D to keep our products at the forefront of innovation
As a source manufacturer,We have 12,000 square meters of production plant, it has cutting-edge manufacturing, and eliminates intermediate links, is not a trader, and can achieve delivery in the shortest possible time, with first-class efficiency.
Support customized R&D power, length, appearance, shaft, OEM, etc., and provide free customized solutions
Use energy-saving and environmentally friendly materials, actively assume the responsibility of protecting the environment, and minimize noise and reduce interference to the surrounding environment.
Resolutely stand on the same front with customers, overcome technical difficulties, and whether it is a salesman or a professional technical team, you can contact anytime and anywhere,resolutely be responsible for the product to the end, and never flinch.
With a number of patent certificates, CC, FCC, etc., the quality is reliable and guaranteed, although each independent motor is a part, but each part will also go through layers of testing, only the perfect product will successfully appear on the road of transportation.
Our motors are widely used in the United States, Germany, Japan, Italy, Argentina, Australia, etc., and we are the first choice for engineers and purchasing managers everywhere looking for high-precision, high-performance, low-noise motors.
We have been widely praised by customers, whether it is product quality, or after-sales response service, we have been recognized by customers, won wide appreciation, and are called "dear friends" by them, and even will visit internationally because of technical problems
Archimedes once said, give me a fulcrum, and I will lift the whole earth. Then I would like to say, give BG Motor a chance and give you back a perfect piece!